Imagine using one phone line to do many things like talk to someone, send messages, and even make video calls. That’s what ISDN allowed people to do.
So, what is ISDN and why was it so special?
A long time ago, phone lines could only be used for voice calls, and they were very slow. But then ISDN came in. It stands for Integrated Services Digital Network. It changed everything by letting people use one phone line to send voice, video, and data all at once and much faster.
ISDN helped people and businesses talk and share information more easily. And even today, it’s still used in some places where internet is not strong.
Let’s find out what ISDN is and how it works.
What is ISDN?
ISDN, or Integrated Services Digital Network, is a communication technology that allows voice calls, video calls, and data to be sent digitally over regular telephone lines.
In simple terms, ISDN is a system that upgrades old phone lines so they can do more than just voice calls. It uses digital signals instead of older analog signals, which makes the connection faster, clearer, and more reliable.
With ISDN, you can use one line to make phone calls, send files, and even do video conferencing all at the same time. This made it very popular with businesses before high-speed internet (like broadband) became common.
So, ISDN is basically a smarter, more powerful version of a regular telephone line, designed to handle different types of communication at once.
How Does ISDN Work?
ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) works by converting traditional analog signals into digital signals, making communication faster, clearer, and more reliable.
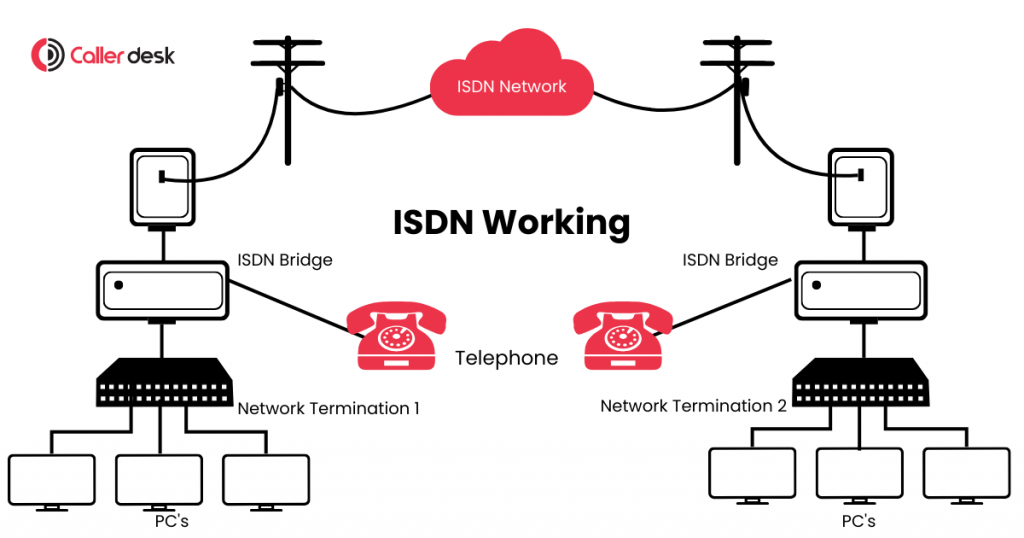
Unlike older phone systems that could only carry voice, ISDN allows multiple services like voice calls, video calls, and data transfers to happen at the same time on a single line.
Types of ISDN:
There are two types of ISDN networks, depending on how much data you need to send:
1. Basic Rate Interface (BRI)
- 2 B channels (64 Kbps each) for voice, video, or data transfer.
- 1 D channel (16 Kbps) for call control and management.
- Perfect for home users and small businesses that don’t need a massive connection.
2. Primary Rate Interface (PRI)
- 23 B channels (64 Kbps each) + 1 D channel (64 Kbps) in North America.
- 30 B channels + 1 D channel in Europe.
- Ideal for big companies, call centers, and high-volume communication needs.
Is ISDN Still Used Today?
Even though broadband and fiber optics have become popular, ISDN is still used in some places. It is reliable and works well where modern internet services are unavailable or when businesses need a backup connection.
1. Backup Connection (When the Internet Fails)
- Businesses use ISDN lines as a backup in case broadband stops working.
- It provides a stable and secure connection during network failures.
2. Remote Areas (Where Broadband is Limited)
- ISDN is useful in rural areas where high-speed internet is not available.
- It allows clear voice calls and data transfer even in remote locations.
3. Special Industries (Where Stability is Needed)
- TV and radio stations use ISDN networks for high-quality voice and video calls.
- Banks and government offices use it for secure and reliable communication.
For regular users, ISDN is mostly replaced by broadband. But in areas where internet service is weak, or for industries needing stable communication, ISDN is still valuable.
ISDN vs. Modern Alternatives
Over the years, ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) has been replaced by broadband and VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) because they offer faster speeds and lower costs. Most businesses and individuals now prefer these modern technologies.
However, ISDN is still used in some industries and remote areas where reliability is important.
ISDN vs. Broadband vs. VoIP – A Quick Comparison
| Feature | ISDN | Broadband | VoIP |
| Speed | Up to 128 Kbps (BRI) | Up to 100 Mbps or more | Dependent on broadband speed |
| Reliability | Very reliable (stable and secure) | Can be unstable (depends on service provider) | Dependent on broadband reliability |
| Setup Cost | Higher | Lower | Lower (often bundled with broadband) |
| Use Cases | Specialized, backup | General internet use | General, primary connection |
How is ISDN Different from PSTN?
People often ask, what is the difference between ISDN and PSTN? Here’s a simple answer:
- PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) uses analog signals, which means it can only handle voice calls.
- ISDN converts signals into digital, so it can send voice, video, and data at the same time.
This made ISDN an example of a network that improved communication before broadband became common.
Conclusion
With the rise of broadband and VoIP, ISDN might seem outdated, but it still plays a role in specific situations.
The strong reliability of ISDN networks makes them useful in remote areas where broadband isn’t available and as a backup option for businesses. Industries like broadcasting and banking still use ISDN because of its stable and secure communication.
While broadband and VoIP offer higher speeds and flexibility, ISDN stands out for its dependability. This shows how technology evolves each innovation has its own place and purpose in the digital world.





